CFD study of heat transfer reduction using multiple injectors in a DCEE concept
G. Nyrenstedt, T. Alturkestani, H.G. Im, B. Johansson
SAE Technical Paper, 2019-01-0070, (2019)
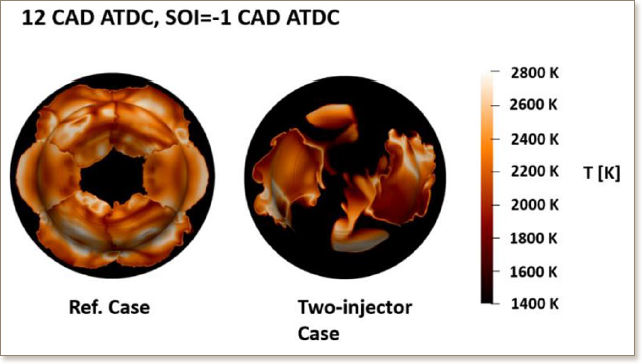
Earlier studies on efficiency improvement in CI engines have suggested that heat transfer losses contribute largely to the total energy losses. Fuel impingement on the cylinder walls is typically associated with high heat transfer. This study proposes a two-injector concept to reduce heat losses and thereby improve efficiency. The two injectors are placed at the rim of the bowl to change the spray pattern. Computational simulations based on the Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes approach have been performed for four different fuel injection timings in order to quantify the reduction in heat losses for the proposed concept. Two-injector concepts were compared to reference cases using only one centrally mounted injector. All simulations were performed in a double compression expansion engine (DCEE) concept using the Volvo D13 single-cylinder engine. In the DCEE, a large portion of the exhaust energy is re-used in the second expansion, thus increasing the thermodynamic efficiency. To isolate the heat losses associated with the changed spray pattern of the two-injector concept, effects of the heat release are excluded during the analysis. Results showed that the optimal injection strategy allows a decrease in the temperature close to the walls, leading to heat loss reduction up to 13 % or 2 % of the fuel energy. The residual exhaust energy was increased by 1.5 %-points with the two-injector concept when compared to the reference case. This proved the advantage of the two-injector concept compared to conventional single injector case for the DCEE application.